Seed Oils, Hormones & Low Iron: The Real Reason Your Ferritin Looks “Normal” But You’re Exhausted
🛢️ Seed Oils & Iron Deficiency: The Hidden Link Sabotaging Your Energy
If your energy wheel keeps buffering by 2 p.m., your hairbrush looks like it pays rent, and your cycle is auditioning for a crime scene—no, you’re not “just getting older.” 📉
Plot twist: it might be your cooking oil. Industrial seed oils (canola, soybean, corn, sunflower, safflower) are the quiet saboteurs—nudging inflammation, draining nutrients, and whispering to your hormones, “let’s be extra.” The result? metabolic chaos® that blocks iron absorption and leaves you tired, brittle, and over it.
I’m not here for shame; I’m here for data. This is your no-nonsense decode through a Functional Diagnostic Nutrition® + Traditional Naturopathic lens—faith-aligned, science-forward, and laser-focused on uncovering your healing opportunities.
⚗️ Seed Oils 101: Why They’re Uniquely Problematic (Quick Science You’ll Actually Remember)
Ultra-processed (“RBD”): Refined-Bleached-Deodorized with heat/solvents → protective phytonutrients stripped; small amounts of oxidation byproducts can form before cooking.
High in linoleic acid (LA, omega-6 PUFA): LA is chemically fragile. Heat, light, and oxygen turn it into lipid peroxides and aldehydes (e.g., 4-HNE, MDA) that stress cells and the liver.
Inflammatory eicosanoids: Excess LA converts to arachidonic acid (AA), feeding pro-inflammatory eicosanoids (PGE₂, leukotrienes).
Membrane remodeling: PUFAs embed into cell + mitochondrial membranes. More fragile fats = more oxidative wear, slower receptors, tired mitochondria.
Omega-ratio distortion: When LA crowds out omega-3s, your baseline shifts toward inflammation.
Translation: seed oils quietly raise oxidative stress + inflammation, which rewires iron handling, hormones, and energy.
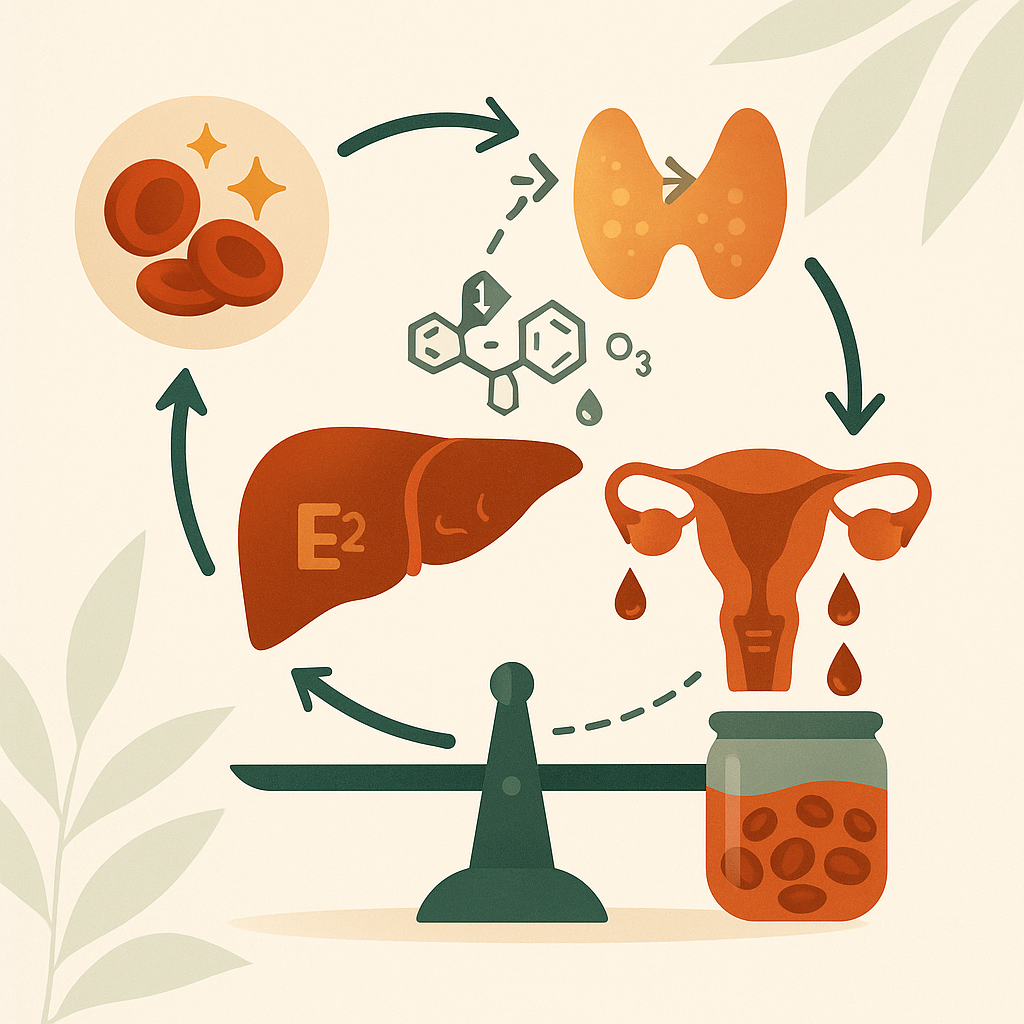
🧬 How Seed Oils Create the Perfect Storm for Low Iron, Ferritin & Hemoglobin
1) 🔥 Inflammation → Hepcidin ↑ → Iron “Lockdown”
Excess omega-6 LA and its oxidized metabolites stimulate cytokines (esp. IL-6). IL-6 triggers hepcidin, the liver hormone that:
Blocks intestinal iron absorption, and
Traps iron in storage so tissues can’t use it.
What you might see on labs:
Ferritin can be normal or high (it’s an acute-phase reactant) while hemoglobin, serum iron, and % saturation are low → classic anemia of inflammation.
Ferritin note: Ferritin may range low → “normal.” In true iron-deficiency anemia with low hemoglobin, ferritin is often low—unless inflammation is artificially elevating it.
2) 🧠 Liver Congestion → Poor Iron Recycling
Oxidized seed oils generate lipid peroxides the liver must neutralize. That load can:
Jam iron recycling via macrophages,
Impair transferrin (iron transport),
Raise demand for B12/folate (methylation) needed for heme synthesis.
Result: you’re eating iron, but the “distribution system” is stalled.
3) 🧻 Gut Integrity → Absorption Down
Seed-oil-heavy, ultra-processed foods:
Disrupt the microbiome (vital for mineral absorption),
Increase intestinal permeability (leaky gut), and
Can lower stomach acid, which you need to liberate non-heme iron from plants.
If you already wrestle with bloat, IBS/SIBO, or low HCl, absorption falls even more.
4) 🚫 Processed Add-Ons → Anti-Nutrient Pile-On
Seed oils rarely travel solo. The same foods bring phytates, oxalates, and added calcium that block iron uptake, while displacing lentils, pumpkin seeds, leafy greens, and vitamin-C-rich produce that improve absorption.
5) 🧯 The Nutrient-Drain Loop (Why You Feel Worse)
Because PUFAs oxidize easily, your body “spends” nutrients to put out fires:
Vitamin E → first-line defense against lipid peroxyl radicals
Vitamin C → recycles vitamin E; buffers oxidative stress
Glutathione / NAC → neutralizes peroxides; supports liver detox
Mineral cofactors:
Zinc + Copper → superoxide dismutase (antioxidant enzyme)
Selenium → glutathione peroxidase (breaks down lipid peroxides)
Magnesium → hundreds of reactions incl. energy + methylation
B12 + Folate → RBC maturation & heme synthesis
Seed oils can deplete the very nutrients you need to build and protect red blood cells.
6) 💢 Hormone Disruption (Heavy Periods, Fatigue, Mood)
Inflammation + oxidative stress from seed oils ripple through endocrine systems:
Estrogen dominance: Inflammatory signals (e.g., PGE₂) can increase aromatase, raising local estrogen → heavier cycles → more iron loss.
Lower SHBG: Liver stress reduces sex-hormone-binding globulin, increasing swings in free estrogen/testosterone (PMS, acne, mood).
Thyroid drag: The liver converts T4 → active T3. Oxidative stress slows this, worsening fatigue and low stomach acid—both hurt iron status.
Insulin signaling: Oxidized membranes + eicosanoids blunt insulin sensitivity. Blood-sugar swings drive more inflammation → more hepcidin.
Mitochondrial meh: PUFA-rich fragile membranes = sluggish receptors + low ATP → tired everything.
Net effect: Heavier periods + poorer absorption + nutrient drain + hepcidin block = the perfect storm for low hemoglobin, iron, and ferritin.
🧠 Fun Fact
Iron is a hormone helper. It powers the thyroid’s T4→T3 conversion and fuels liver enzymes that clear estrogen. When iron runs low, thyroid slows and estrogen lingers—then heavier periods drain even more iron. 🔄
Translation: Balance iron ↔ balance hormones.
🚩 Signs Your Iron Status Needs a Deeper Look
Non-refreshing fatigue, brain fog
Shortness of breath, dizziness, palpitations
Hair shedding, brittle nails, cold hands/feet
Heavy or prolonged periods
Poor wound healing or easy bruising
🧪 Functional Testing: Test, Don’t Guess
Core Iron / Anemia Workup
Complete Blood Count (CBC): Hemoglobin (Hgb), RBC count, and indices MCV, MCH, MCHC, RDW (classify anemia pattern).
Iron Studies: Serum Iron, Ferritin, Total Iron-Binding Capacity (TIBC), and Transferrin % Saturation.
Vitamin B12 & Folate (rule out megaloblastic anemia; support methylation/heme).
Reticulocyte Count (bone-marrow response).
Peripheral Blood Smear (RBC morphology clues).
Additional tests as indicated: renal/liver function; targeted genetics.
Ferritin reality check: Ferritin can appear normal in inflammation. With low hemoglobin, ferritin is often low unless hepcidin/inflammation is masking deficiency.
🔬 Additional Functional Labs (keep these)
GI-MAP® or Gut Zoomer: Malabsorption, pathogens, intestinal permeability.
DUTCH Complete®: Estrogen dominance + cortisol patterns (heavy bleeding = iron loss).
Nutrigenomics (DNAlife): MTHFR, TMPRSS6, HFE—methylation, iron regulation/transport.
🧾 What Each Marker Means (FBCA cheat sheet)
Hgb (Hemoglobin): Oxygen-carrying protein in RBCs; low = anemia.
Hct (Hematocrit): % of blood that’s RBCs; low in anemia/dilution.
Serum Iron: Circulating iron at that moment; low in many anemias.
Ferritin: Storage iron; low = deficiency. Normal/high can reflect inflammation.
TIBC: Capacity to bind iron; high often = iron deficiency; low with inflammation.
% Saturation: How much transferrin is carrying iron; low = deficiency/poor use.
RDW: Size variation of RBCs; high = mixed deficiencies/early anemia.
MCV: RBC size; low microcytic (iron); high macrocytic (B12/folate).
MCHC: Hemoglobin concentration; helps refine anemia type.
🌱 Plant-Based Iron Rebuild
1) Swap the Oils
Choose low-inflammatory, minimally processed options:
🫒 Extra-virgin olive oil (dressings/low heat)
🥥 Coconut oil (heat-stable)
🥑 Avocado oil (moderate heat; look for low-LA brands)
🌿 Flaxseed oil (cold only)
…then favor whole-food fats: avocado, olives, nuts/seeds.
2) Eat to Absorb (Not Just Consume)
Iron-rich plants: Lentils, chickpeas, white/black beans, quinoa, pumpkin seeds, sesame/tahini, spinach/chard, blackstrap molasses.
Vitamin C boosters at meals: Citrus, berries, kiwi, bell pepper, broccoli → dramatically increase non-heme iron absorption.
Folate/B-complex foods: Dark leafy greens, beets, legumes.
Timing matters: Keep coffee/tea and calcium-fortified foods 1–2 hours away from iron-rich meals.
3) Gentle, Targeted Supplementation*
Iron bisglycinate or plant-based iron (well-tolerated; dose by labs)
Magnesium, Zinc, Copper (iron-enzyme cofactors)
NAC or Glutathione (lower oxidative/liver burden)
*Please don’t megadose iron blindly—test, personalize, re-test.
4) Support the Liver, Calm Inflammation
Bitter greens, crucifers, beets, lemon water, herbs/spices (rosemary, turmeric, ginger).
Prioritize sleep, consistent stress rhythms, and moderate movement.
Minimize reheated restaurant oils and deep-fried foods (aldehydes skyrocket with reuse).
🌿 Faith-Rooted Bottom Line
God designed your body to renew. When we remove interferences (seed-oil-heavy processed foods, unmanaged stress, hidden gut issues) and supply what’s missing (nutrients, rest, rhythm), we uncover healing opportunities—and the energy you’ve been praying for.
“The life of the body is in the blood.” — Leviticus 17:11
🙋🏽♀️ Ready to Stop Guessing and Start Healing?
Let’s run the right labs, read them through a functional lens, and build your WFPB plan that honors your biology and your beliefs.
👉🏾 Book a consultation to get your personalized lab roadmap and protocol.
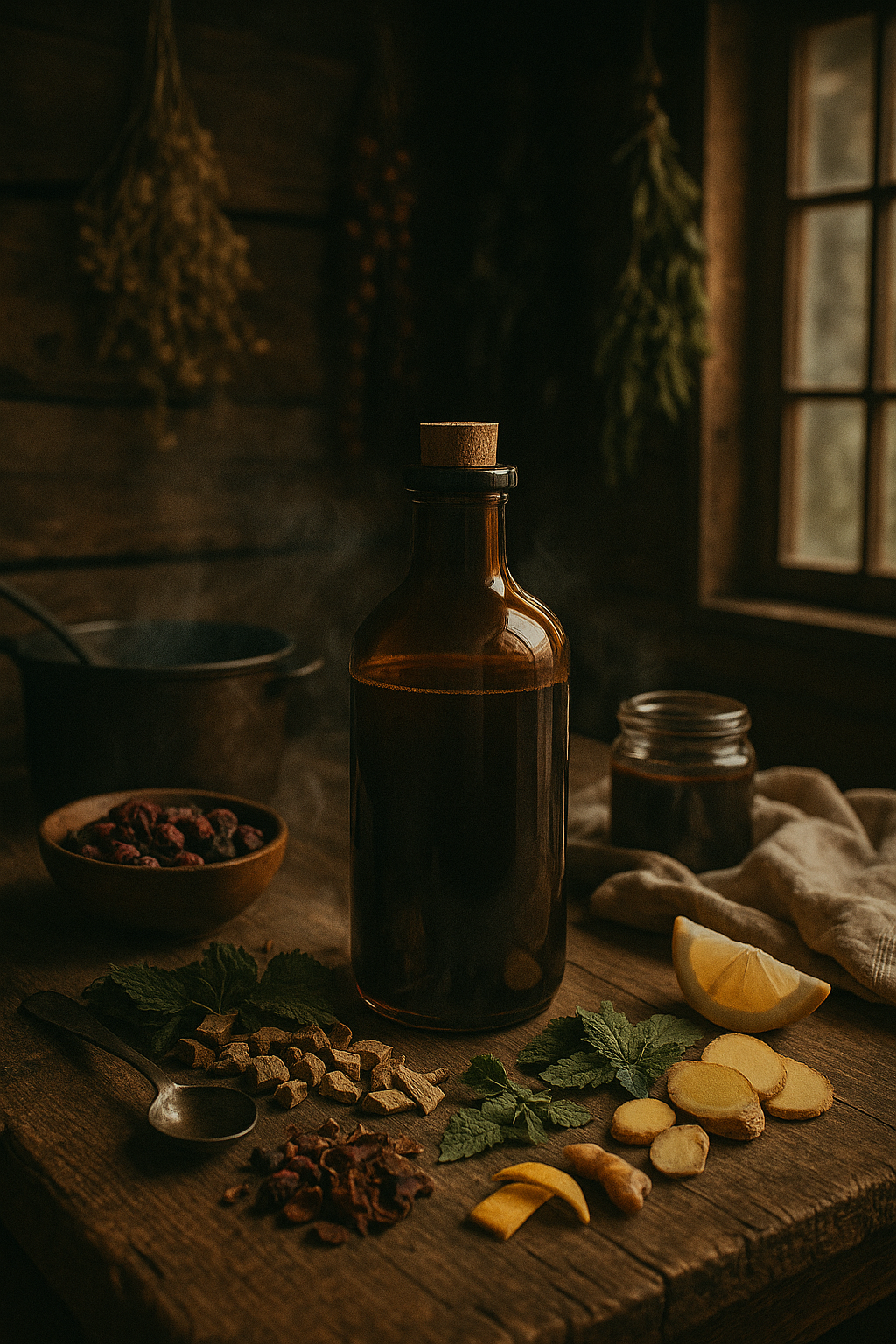
🩸Harmony Herbal Mineral Syrup (WFPB, alcohol-free) 🌿
Here’s a Floradix®-inspired, alcohol-free, whole-food plant-based iron elixir/syrup you can make at home. It echoes the spirit of a liquid herbal iron tonic—gentle, absorbable, and paired with vitamin-C–rich botanicals—without animal products or synthetic flavors.
🛒 Shopping List
Mineral & blood-building herbs
🌿 Yellow dock root (cut/sifted) – 10 g
🌿 Nettle leaf – 10 g
🌿 Dandelion leaf – 6 g
🌿 (Optional) Alfalfa leaf – 4 g
Vitamin-C & flavor boosters
🌹 Rose hips – 8 g
🌺 Hibiscus petals – 6 g (or 🍈 amla powder 1–2 tsp off-heat for a low-histamine option)
🍊 Orange peel (bitter/sweet) – 2 g
🫚 Fresh ginger, sliced – 3 g
Syrup base
💧 Water – 1.25 L
🍯 Blackstrap molasses – 180 ml
🌴 Date syrup (or prune concentrate) – 120 ml
🍃 Vegetable glycerin (USP) – 150 ml
🍋 Lemon juice – 30 ml
🧂 Pinch of fine sea salt
🥤 (Optional) Beet juice concentrate – 60 ml
⚡ (Optional) Ionic trace minerals – 10–20 drops (unsweetened)
👩🏾🍳 Method
🔥 Decoct “hard” botanicals (30 min):
Add water + yellow dock + ginger + orange peel to a non-reactive pot. Cover; gentle simmer 30 min.🌿 Add mineral leaves (10 min):
Stir in nettle + dandelion (+ alfalfa). Low simmer 10 min, covered.🍊 Vitamin-C steep (15 min, off heat):
Turn off heat. Add rose hips + hibiscus (or amla). Cover; steep 15 min.🥣 Strain & reduce:
Strain through fine sieve/cheesecloth; press herbs. If >700 ml, simmer gently to ~500 ml.🧪 Finish the syrup (no boil):
Off heat, whisk in molasses + date/prune syrup + glycerin + lemon + salt (+ optional beet/trace minerals).🧴 Bottle & store:
Funnel hot into sterilized amber bottles. Cool, label, refrigerate.
⏳ Shelf life: 3–4 weeks (glycerin + acidity). Without glycerin: 7–10 days.
🥄 Serving Suggestions*
👩🦰 Adults: 1 Tbsp (15 ml) 1–2× daily with/after meals with vitamin-C foods.
🧒 Kids 6–12: 1 tsp (5 ml) daily with pediatric guidance.
🔁 Consider “5 days on / 2 days off”. Re-check labs after 6–8 weeks with your clinician.
*Education only; not medical advice. Avoid if you have iron overload (e.g., hemochromatosis). Always coordinate with your provider.
💡 Why These Ingredients
🍯 Blackstrap molasses: food-based iron + minerals; gentle on the gut.
🌿 Yellow dock: classic naturopathic herb for iron utilization & regularity.
🌿 Nettle & alfalfa: mineral-dense (Fe, Mg, silica) to “build blood.”
🌿 Dandelion leaf: potassium-rich bitter for liver flow.
🌹🌺/🍈 Rose hips & hibiscus / amla: vitamin C → boosts non-heme iron absorption; bright flavor.
🍊🫚 Orange peel & ginger: digestion support, reduce queasiness.
🍃 Glycerin + 🍋 lemon: sweetness, stability, longer fridge life.
🥤 Beet concentrate (opt): color, circulation vibe.
⚡ Trace minerals (opt): cofactors (Mg, Zn, Cu) for iron enzymes.
⚠️ Cautions
🤰 Pregnancy/breastfeeding: use only with provider guidance.
💊 Meds: separate iron-rich syrups from medications by 2+ hours.
🪨 Oxalate-sensitive: choose amla over hibiscus.
🫤 Sensitive GI: halve yellow dock, increase nettle slightly.
🏃 “Sport” Upgrade (optional)
🥥 Add coconut water reduction (simmer 1 cup → ½ cup) in step 5 for natural potassium.
🧪 Stir in ¼ tsp cream of tartar (potassium bitartrate) per batch for gentle electrolytes.
📚 Research Touchpoints
🔥 Inflammation → Hepcidin → Iron “Lockdown”
👉🏾 Hepcidin minireview (mechanisms): https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3782966/
👉🏾 Hepcidin–ferroportin axis (review): https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3706197/
👉🏾 Anemia of inflammation (Blood, ASH): https://ashpublications.org/blood/article/133/1/40/6617/Anemia-of-inflammation
👉🏾 Anemia of inflammation (open-access review): https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5308549/
👉🏾 Hepcidin targets ferroportin for degradation: https://haematologica.org/article/view/5538
📈 Ferritin as an Acute-Phase Reactant
👉🏾 StatPearls—Acute phase reactants (ferritin): https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519570/
👉🏾 StatPearls—Iron (notes on ferritin & inflammation): https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542171/
🧯 Lipid Peroxidation & PUFA By-Products
👉🏾 Lipid peroxidation—biochemistry (review): https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4066722/
👉🏾 4-Hydroxy-nonenal (4-HNE) overview: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4693237/
🦠 Ultra-Processed Foods (UPFs) & the Gut
👉🏾 UPFs & the microbiome (Nutrients, 2024 review): https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/16/11/1738
👉🏾 UPFs, microbiota & inflammation (BMJ umbrella review): https://www.bmj.com/content/384/bmj-2023-077310
🌸 Inflammation → Aromatase → Estrogen (Heavier Periods → Iron Loss)
👉🏾 PGE₂ stimulates aromatase (endometriosis cells): https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article/82/2/600/2823486
👉🏾 PGE₂ regulates aromatase in adipose stromal cells: https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article/88/6/2810/2845614
👉🏾 Obesity → inflammation → aromatase in breast tissue (open access): https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3131426/
🦋 Thyroid ↔ Iron
👉🏾 Relationship between iron deficiency & thyroid function (review): https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10675576/
👉🏾 Nutrition & thyroid function (micronutrients incl. iron): https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11314468/
👉🏾 Nutritional factors & thyroid disease (iron/TPO is heme-dependent): https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/proceedings-of-the-nutrition-society/article/multiple-nutritional-factors-and-thyroid-disease-with-particular-reference-to-autoimmune-thyroid-disease/DBA9BAD5847376FA5E099B7ACC7556A2
🍋 What Helps or Hinders Plant (Non-Heme) Iron Absorption
👉🏾 Vitamin C enhances non-heme iron (AJCN): https://ajcn.nutrition.org/article/S0002-9165(23)06453-5/fulltext
👉🏾 Coffee/tea polyphenols ↓ iron absorption (open access): https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6165914/
👉🏾 Phytate inhibits iron & calcium bioavailability (BMC Nutrition): https://bmcnutr.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40795-016-0064-8
👉🏾Comprehensive review—factors in iron absorption: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9219084/
🧪 Basic Evaluation: What to Order
👉🏾 Iron deficiency evaluation (StatPearls): https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448065/
Blog Disclaimer
The health information on this blog is for general educational purposes only and is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. It should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider before making any health-related decisions
This blog may contain affiliate links, meaning Leaves from the Tree of Life LLC may earn a small commission if you purchase a product or service through these links—at no additional cost to you. Your support helps us continue to provide valuable content. Thank you!